A Comprehensive Guide to Measuring ERP Implementation Success: Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to Track

Introduction
Implementing an ERP system is a significant investment for any organization. At Pabian Partners, we believe if our customer is live and running, the implementation is considered successful. Having said that, degree of success is based on specific needs like for e.g. elimination of external systems for lot tracking, implementation of an MRP based production to replace excel sheets compiled from various reports etc. or in general outlined to improve and add during the discovery process. Once implemented and internal personnel are trained on the system, we keep in close touch with our customers to make sure it is a continued success. In this article, we will show you some effective methods you can put in place to measure and evaluate the outcomes of an implementation process apart from specific goals that have been outlined between the two parties’ customer company and the implementation company (ERP vendor/reseller) and general KPIs to track your progress.
How to Measure Success of an ERP Implementation?
Before implementing an ERP system, it’s essential to establish clear objectives and goals that align with the organization’s strategic priorities. These objectives will serve as benchmarks for measuring success throughout the implementation process. Let’s talk about the top four types of general KPIs you can measure from a high level in this regard:
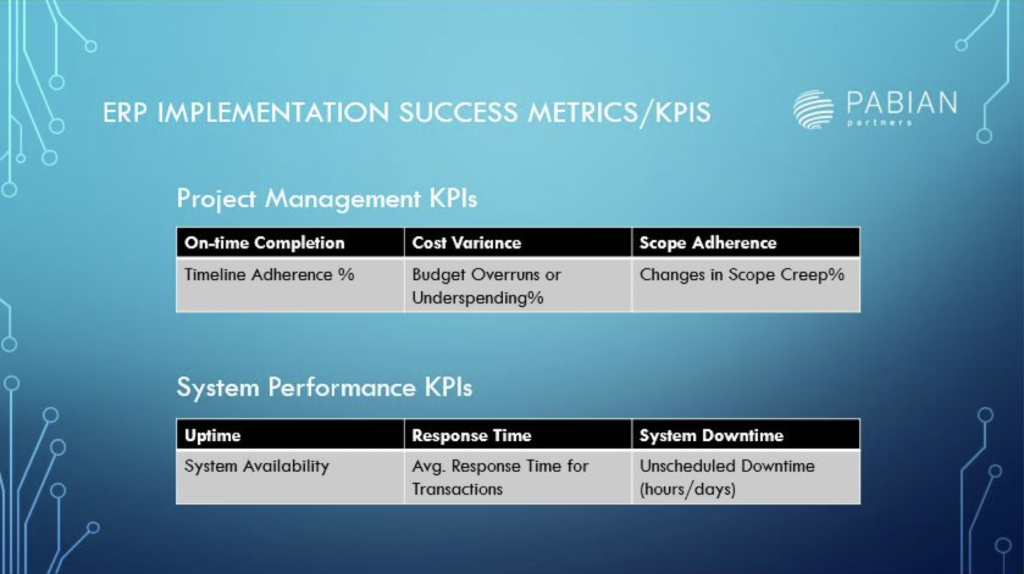
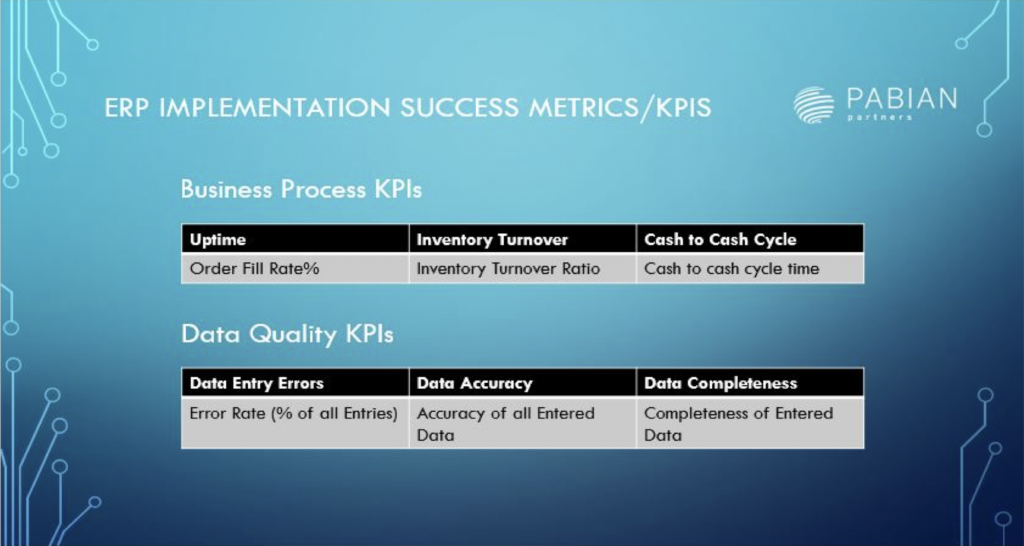
-
- Project Management KPIs: Track the project’s adherence to the initial timeline, budget, and scope. This includes measuring on-time completion percentage, budget variance, and scope adherence.
- System Performance KPIs: Assess the performance of the ERP system, including uptime, response time, and system downtime. This ensures that the system operates efficiently and meets user expectations.
- Business Process KPIs: Evaluate improvements in key business processes such as order fulfillment, inventory turnover, and cash-to-cash cycle time. These metrics indicate the impact of the ERP implementation on operational efficiency.
- Data Quality KPIs: Measure the accuracy and completeness of data entered into the ERP system. High-quality data ensures reliable reporting and decision-making.
- On-time and On-budget Delivery: Measure the implementation timeline and budget against initial estimates. Delays and cost overruns can indicate potential issues in project management or scope creep.
- User Adoption Rates: Track the percentage of employees using the ERP system compared to the total number of users. High user adoption rates indicate successful training and user-friendly interfaces.
- System Performance: Monitor the system’s performance metrics, such as response times, uptime, and system availability. A well-performing ERP system ensures efficient business operations.
- Process Efficiency Improvements: Measure improvements in key business processes, such as order fulfillment time, inventory turnover, or cash conversion cycle. ERP implementation should lead to streamlined processes and increased productivity.
- Data Accuracy and Integrity: Assess the accuracy and integrity of data entered into the ERP system. High-quality data ensures reliable reporting and decision-making.
- Customer Satisfaction: Gather feedback from customers regarding their experience with the organization post-ERP implementation. Higher customer satisfaction scores indicate improved service levels and customer interactions.
- Return on Investment (ROI): Calculate the financial ROI of the ERP implementation by comparing the costs incurred with the benefits gained. This may include cost savings, revenue increases, or efficiency gains.
- Employee Satisfaction and Engagement: Conduct surveys or interviews to gauge employee satisfaction and engagement with the ERP system. Satisfied employees are more likely to use the system effectively and contribute to its success.
- Continuous Monitoring and Improvement: Regularly review and analyze KPI data to identify areas for improvement and optimization. Implement corrective actions and adjustments as needed to enhance system performance and achieve better outcomes. Establish a system for ongoing monitoring and measurement of KPIs even after the initial implementation phase. ERP systems evolve over time, and continuous evaluation is essential for long-term success.
Conclusion
Measuring the success of an ERP implementation requires a comprehensive approach that goes beyond project completion. By defining clear objectives, tracking key performance indicators, and continuously monitoring and improving processes, organizations can ensure that their ERP systems deliver maximum value and contribute to overall business success. Implementing an effective measurement framework allows organizations to identify areas of strength, address challenges, and optimize their ERP systems for long-term growth and competitiveness.

